| Location | E11-G031 |
| Academic Staff in charge | Prof. Chi Tat KWOK; Prof. Kin Ho LO |
| Technician | Po Kee WONG |
| Telephone | (853) 8822-8057, 4292 |
Objective
Lasers have been applied extensively in industry. They are usually used for cutting, welding, drilling, surface modification, etc. The purposes of this laboratory are
- To allow the students to have some ideas of laser technology in manufacturing processes.
- To provide facilities for students’ final projects and MSc and PhD students’ theses.
- To serve local industries.
Facilities
1. Corrosion testers
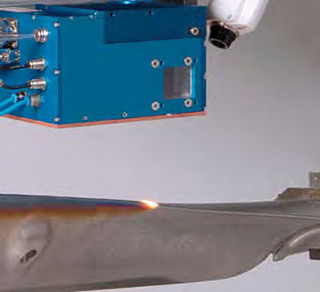
Laser System
The laser system consists of the fiber-couple diode laser module (Laserline LDM 1000-1000) and the CNC XYZ table. Diode laser with near infra wavelength provides high energy absorptivity to metals.
Specifications
| Classification | Class IV |
| Central wavelength | 900 – 990 nm |
| Maximum power | 2300 W |
| Beam quality | 110 mm rad |
| Optical fiber | 1000 μm |
 |
 |
 |
Steps for laser processing:
- Design scanning sequences with the aid of drawing software, such as AutoCAD and Corel Draw.
- The drawing is converted to a CNC program that can be recognized by the controller of the CNC machine.
- Adjust the desired power level and scanning speed of the laser machine.
The laser beam is transmitted through an optical fiber. The high energy beam acts as a heat source and is controlled by the CNC machine for processing.
Applications of laser:
Experiments
- Laser transformation hardening
- Laser surface alloying
- Laser welding
- Laser cutting
Courses supported
| EMEB121 | Engineering Materials |
| EMEB351 | Advanced Materials for Engineers |
| EMEB355 | Corrosion, Wear and Degradation of Materials |
| EMEB410 | Design Projects |
| ELME702 | Physics of Materials |
| ELME717 | Special Topics in Manufacturing I: Laser Materials Processing |
| ELME718 | Special Topics in Manufacturing II : Surface Engineering |